Tutorial 1.2: Gradient descent-based two level optimization
Contents
Tutorial 1.2: Gradient descent-based two level optimization#
Authors: Xiaoyu Xie
Contact: xiaoyuxie2020@u.northwestern.edu
Import libraries#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import matrix_rank
from numpy.linalg import inv
import pandas as pd
import pysindy as ps
import random
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
from scipy.optimize import minimize
random.seed(3)
# # please uncomment these two lines, if you run this code in Colab
# !git clone https://github.com/xiaoyuxie-vico/PyDimension-Book
# %cd PyDimension-Book/examples
Parametric space analysis#
Paraemter list:
\(f(\eta P,V_s,r_0, C_p, \alpha, \rho, T_l-T_0)=e\)
Load dataset#
data = np.loadtxt(
open("../dataset/dataset_keyhole.csv","rb"),
delimiter=',',
skiprows=1,
usecols = (2, 3, 4, 7, 5, 6, 10, 12)
)
X = data[:, :7]
Y = data[:, 7]
Calculate dimension matrix#
Dimension matrix (input):
\begin{equation}
D_{in}=
\left[
\begin{array}{ccc}
2 & 1 & 1 & 2 &2&-3&0\
-3 & -1 & 0 & -2 &-1&0&0\
1& 0 & 0 & 0 &0&1&0\
0& 0 & 0 & -1 &0&0&1\
\end{array}
\right]
\end{equation}
Dimension matrix (output):
\begin{equation}
D_{out}=
\left[
\begin{array}{ccc}
1 \
0 \
0 \
0 \
\end{array}
\right]
\end{equation}
D_in = np.mat('2, 1, 1, 2, 2, -3, 0; -3, -1, 0, -2, -1, 0, 0; 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0; 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1')
D_out = np.mat('1; 0; 0; 0')
D_in_rank = matrix_rank(D_in)
print(D_in_rank)
4
Calculate basis vectors#
Calculate three basis vectors for equation: \( D_{in}x=0 \)
Din1 = D_in[:, 0:4]
Din2 = D_in[:, 4:8]
x2 = np.mat('-1; 0; 0')
x1 = -inv(Din1) * Din2 * x2
basis1_in = np.vstack((x1, x2))
print(f'basis1_in: \n{basis1_in}')
x2 = np.mat('0;-1;0')
x1 = -inv(Din1) * Din2 * x2
basis2_in = np.vstack((x1, x2))
print(f'basis2_in: \n{basis2_in}')
x2 = np.mat('0; 0; -1')
x1 = -inv(Din1) * Din2 * x2
basis3_in = np.vstack((x1, x2))
print(f'basis3_in: \n{basis3_in}')
basis1_in:
[[ 0.]
[ 1.]
[ 1.]
[ 0.]
[-1.]
[ 0.]
[ 0.]]
basis2_in:
[[ 1.]
[-3.]
[-2.]
[ 0.]
[ 0.]
[-1.]
[ 0.]]
basis3_in:
[[ 0.]
[ 2.]
[ 0.]
[-1.]
[ 0.]
[ 0.]
[-1.]]
Helper functions#
def calc_pi(a):
'''
Calculate pi
Note that the best coef for keyhole is [0.5, 1, 1]
'''
coef_pi = 0.5 * basis1_in + a[0] * basis2_in + a[1] * basis3_in
pi_mat = np.exp(np.log(X).dot(coef_pi))
pi = np.squeeze(np.asarray(pi_mat))
return pi
def calc_y(a, w):
'''
Calculate the prediction y using a polynomial function
'''
pi = calc_pi(a)
y = w[0] + w[1] * pi + w[2] * pi**2 + w[3] * pi**3 + w[4] * pi**4 + w[5] * pi**5
return y
def objective(a, w):
'''
Calculate objective(loss)
'''
return np.square(pi2 - calc_y(a, w)).mean()
def ploter(pi1, pi2, iteration):
'''
Visualization
'''
fig = plt.figure()
plt.scatter(pi1, pi2)
plt.xlabel(r'$\Pi_1$', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabel(r'$\Pi_2$', fontsize=16)
plt.title(f'Iteration: {iteration}', fontsize=24)
plt.show()
Best representation learning discovery#
niter = 3000
ninital = 1
degree = 5 # polynomial order
a = np.zeros(2)
w = np.zeros(degree + 1)
global pi2
pi2 = Y / X[:,2]
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree)
for j in range(ninital):
a[0] = 2 * random.random()
a[1] = 2 * random.random()
print(f'Initial a={a}')
info = {}
info['initial'] = a
a_history = np.zeros((niter, 2))
model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False)
for i in range(niter):
# level 1: update coefficient w for polynomials
pi1 = calc_pi(a)
pi1_poly = poly.fit_transform(pi1.reshape(-1, 1))
model.fit(pi1_poly, pi2)
coeffi = model.coef_
w = coeffi
y_recover = calc_y(a, w)
r2 = r2_score(y_recover, pi2)
# level 2: update coefficient a for pi
solution = minimize(objective, a, method='BFGS', tol=1e-3, args=w, options={'maxiter':1})
a = solution.x
y_recover = calc_y(a, w)
r2 = r2_score(y_recover, pi2)
a_history[i,:] = a
if i % int(niter // 3) == 0:
# Note that the best coef in keyhole case is [0.5, 1, 1]
# here we only optimize the last two coefficients
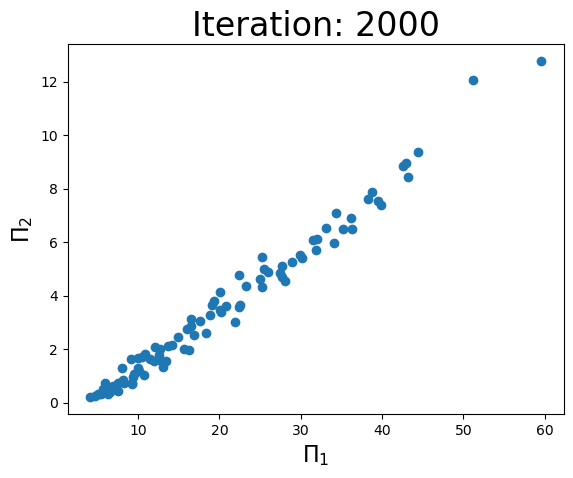
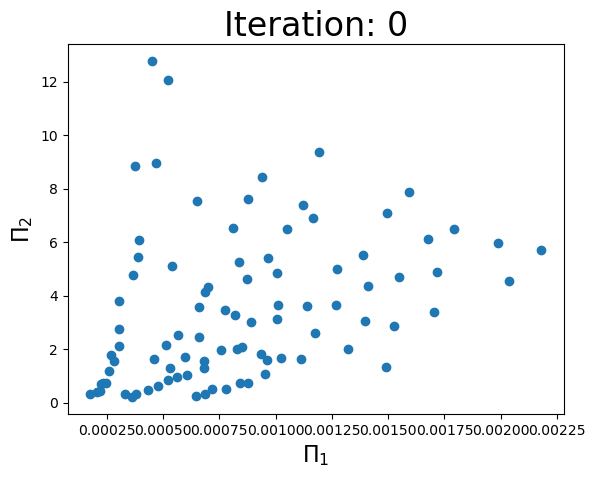
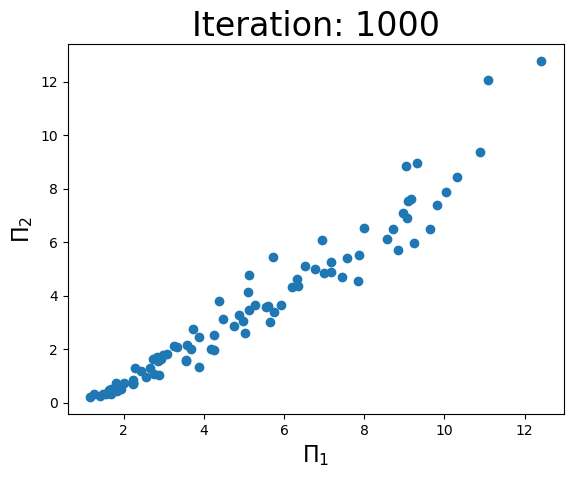
print(f'Iteration: {i}, coef: {a}, Objective: {objective(a,w)}, r2: {r2}')
ploter(pi1, pi2, i)
Initial a=[0.47592925 1.08845845]
Iteration: 0, coef: [0.47655508 1.08822897], Objective: 6.774411431102805, r2: -6.029830431357665
Iteration: 1000, coef: [0.83210715 0.91871379], Objective: 0.34713452499937103, r2: 0.9535269294147469
Iteration: 2000, coef: [0.88125833 0.8855296 ], Objective: 0.10920698118338781, r2: 0.9857184358093292