Tutorial 2.1: ODEs discovery in spring-mass-damper systems!
Contents
Tutorial 2.1: ODEs discovery in spring-mass-damper systems!#
Authors: Xiaoyu Xie
Contact: xiaoyuxie2020@u.northwestern.edu
In this tutorial, we will go through an example to show how to combine dimensionless learning with SINDy to discover the governing equation in spring-mass-damper systems.
We consider an object with mass \(m\) is suspended from a spring with an initial displacement \(\delta\), a spring constant \(k\), and a damping coefficient \(c\). The schematic of a spring-mass-damper system is shown below:
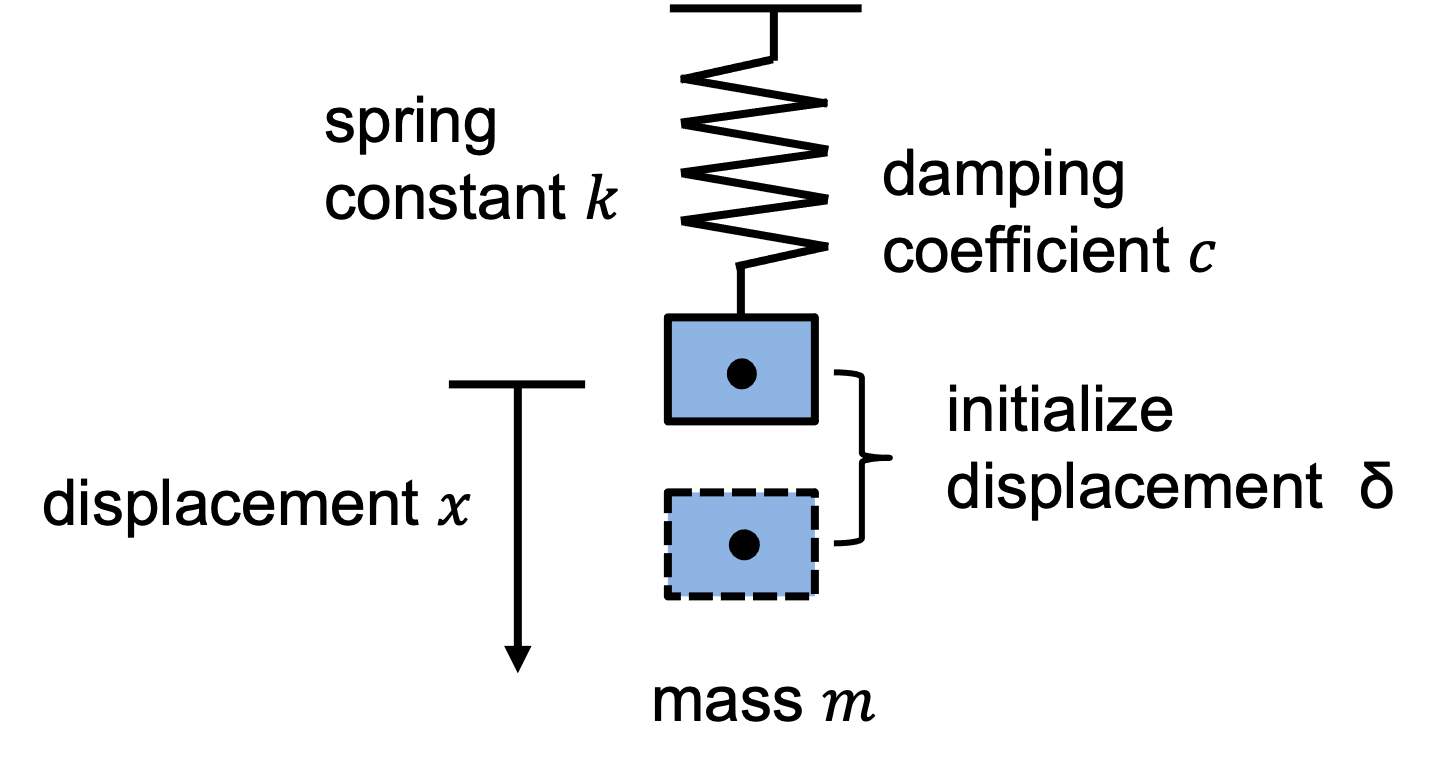
We can express the above system mathematically. The governing equation is
The spring has a initial displacement \(x(t=0)=\delta\) and no initial velocity \(\frac{dx}{dt}=0\).
To create a dataset, we will change \(\delta\), \(m\), \(k\), and \(c\) to obtain different time-varying curves.
Import python libraries#
import copy
import os
import sys
import pandas as pd
from pyexpat import model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, Ridge, LassoCV
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
from sympy.utilities.lambdify import lambdify
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "Arial"
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
# # please uncomment these two lines, if you run this code in Colab
# !git clone https://github.com/xiaoyuxie-vico/PyDimension-Book
# %cd PyDimension-Book/examples
Helper functions#
SeqReg() is a class to identify differential equations using sparse regression.
class SeqReg(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def normalize(self, X, y):
'''
Normalization the data
'''
norm_coef_X = np.mean(np.abs(np.mean(X, axis=0)))
norm_coef_y = np.mean(np.abs(np.mean(y, axis=0)))
norm_coef = min(norm_coef_X, norm_coef_y)
# print('Before X', pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([X, y], axis=1)).describe())
X = X / norm_coef
y = y / norm_coef
# print('After X', pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([X, y], axis=1)).describe())
return X, y
def fit_fixed_threshold(self, X, y, alpha=1.0, threshold=0.005, is_normalize=True):
if is_normalize:
X, y = self.normalize(X, y)
# initialize a linear regression model
# model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False)
model = Ridge(fit_intercept=False, alpha=1)
model.fit(X, y)
# r2 = model.score(X, y)
for idx in range(3):
coef = model.coef_
flag = np.repeat((np.abs(coef) > threshold).astype(int).reshape(1,-1),
X.shape[0], axis=0)
X1 = copy.copy(X)
X1 = np.multiply(X1, flag)
model.fit(X1, y)
r2 = model.score(X1, y)
print(f'training {idx} r2: {r2}')
coef = np.squeeze(model.coef_)
return coef, X1
def fit_dynamic_thresh(self, X, y, non_zero_term=4, alpha=1.0, threshold=0.005,
is_normalize=True, fit_intercept=False, model_name='Ridge', max_iter=200):
'''
decrease the threshold when there are only limited non-zero terms
and increase the threshold when thre are more non-zeros terms
'''
if is_normalize:
X, y = self.normalize(X, y)
# initialize a linear regression model
if model_name == 'Ridge':
model = Ridge(fit_intercept=fit_intercept, alpha=alpha)
elif model_name == 'LR':
model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=fit_intercept)
else:
raise Exception('Wrong model_name.')
model.fit(X, y)
count = 0
while count <= max_iter:
coef = model.coef_
flag = np.repeat((np.abs(coef) > threshold).astype(int).reshape(1,-1),
X.shape[0], axis=0)
cur_non_zero_term = np.sum(flag[0,:])
X1 = copy.copy(X)
X1 = np.multiply(X1, flag)
model.fit(X1, y)
r2 = model.score(X1, y)
# print(f'training r2: {r2}, threshold: {threshold}, cur_non_zero_term: {cur_non_zero_term}')
if cur_non_zero_term == non_zero_term:
break
elif cur_non_zero_term < non_zero_term:
threshold *= 0.95
else:
threshold *= 1.05
count += 1
coef = np.squeeze(model.coef_)
if fit_intercept:
coef_list = coef.tolist()
coef_list.append(float(model.intercept_))
coef = np.array(coef_list)
return coef, X1, r2
PolyDiffPoint()is used to calculate derivatives using polynomial functions.
def PolyDiffPoint(u, x, deg=3, diff=1, index=None):
'''
Poly diff
The original code of this part: https://github.com/snagcliffs/PDE-FIND
'''
n = len(x)
# if index == None: index = int((n-1)/2)
if index == None: index = (n-1)//2
# Fit to a polynomial
poly = np.polynomial.chebyshev.Chebyshev.fit(x, u, deg)
# Take derivatives
derivatives = []
for d in range(1, diff + 1):
derivatives.append(poly.deriv(m=d)(x[index]))
return derivatives
Dataset preparation#
SpringMassDataset() is a class to generate simualtion data set.
class SpringMassDataset(object):
'''
Generate data for spring-mass-damping systems
'''
def __init__(self, k, m, A0, c, v0=0, et=20, Nt=800):
super(SpringMassDataset, self).__init__()
self.k = k
self.m = m
self.A0 = A0
self.c = c
self.et = et
self.v0 = v0
self.Nt = Nt
self.omega_n = np.sqrt(k / m)
self.xi = c / 2 / np.sqrt(m * k)
self.omega_d = self.omega_n * np.sqrt(1 - self.xi**2)
self.A = np.sqrt(A0**2 + ((v0 + self.xi * self.omega_n * A0) / self.omega_d)**2)
self.phi = np.arctan(self.omega_d * A0 / (v0 + self.xi * self.omega_n * A0))
def solution(self):
t = np.linspace(0, self.et, self.Nt, endpoint=False)
x = self.A * np.exp(-self.xi * self.omega_n * t) * np.sin(self.omega_d * t + self.phi)
info = {'t': t, 'x': x}
df = pd.DataFrame(info)
return df
# test the SpringMassDataset
k, m, A0, c, et, Nt = 0.2, 0.2, 0.07, 0.02, 20, 1000
dataset = SpringMassDataset(k, m, A0, c)
data_old = dataset.solution()
fig = plt.figure()
plt.plot(data_old['t'], data_old['x'])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f2190ca42d0>]
FitEqu() is used for generating and parsing the dataset, build the regression library, and identifying the best differential equations.
class FitEqu(object):
'''
For a given data, fit the governing equation.
'''
def __init__(self):
super(FitEqu, self).__init__()
def prepare_data(self, k, m, A0, c, et, Nt):
'''
generate the dataset
'''
dataset = SpringMassDataset(k, m, A0, c, et=et, Nt=Nt)
data = dataset.solution() # {'t': t, 'x': x}
return data
def cal_derivatives(self, data, dt, Nt, deg=3, num_points=100, boundary_t=5):
'''
prepare library for regression
'''
x_clean = data['x'].to_numpy()
t = np.arange(2*boundary_t, Nt-2*boundary_t)
# points = np.random.choice(t, num_points, replace=False)
points = t
num_points = points.shape[0]
x = np.zeros((num_points, 1))
xt = np.zeros((num_points, 1))
xtt = np.zeros((num_points, 1))
Nt_sample = 2 * boundary_t - 1
for p in range(num_points):
t = points[p]
x[p] = x_clean[t]
x_part = x_clean[t-int((Nt_sample-1)/2): t+int((Nt_sample+1)/2)]
xt[p], xtt[p] = PolyDiffPoint(x_part, np.arange(Nt_sample)*dt, deg, 2)
return x, xt, xtt
@staticmethod
def build_library(x, xt, xtt):
'''
build the library for sparse regression
'''
X_library = [
x,
xtt,
x**2,
np.multiply(x.reshape(-1, 1), xt.reshape(-1, 1)),
np.multiply(x.reshape(-1, 1), xtt.reshape(-1, 1)),
]
X_library = np.squeeze(np.stack(X_library, axis=-1))
names = ['x', 'xtt', 'x^2', 'x*xt', 'x*xtt']
y_library = xt
return X_library, y_library, names
@staticmethod
def fit(X_library, y_library, threshold=0.002):
'''
squential threshold with dynamic threshold
'''
model = SeqReg()
coef, _, r2 = model.fit_dynamic_thresh(X_library, y_library,
is_normalize=False, non_zero_term=2, threshold=threshold, fit_intercept=False, model_name='LR')
print('Fitting r2', r2)
return coef
def prepare_dataset(is_show=False):
'''
prepare a sets of dataset with different parameters
'''
data = []
fit_equ = FitEqu()
# k, m, A0, c, et, Nt
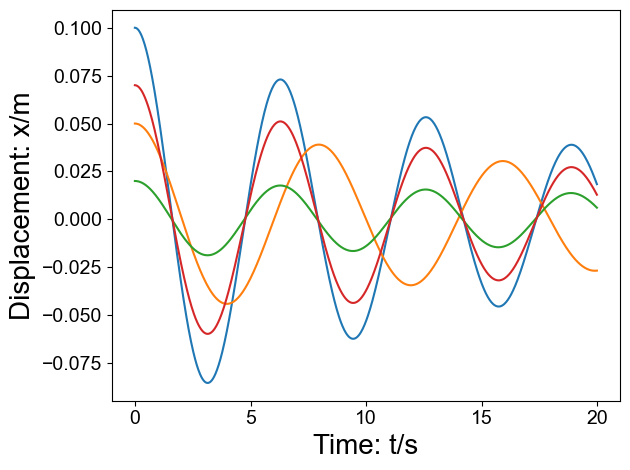
params = [
[1, 1, 0.1, 0.1, 20, 800],
[0.5, 0.8, 0.05, 0.05, 20, 800],
[0.1, 0.1, 0.02, 0.004, 20, 800],
[0.2, 0.2, 0.07, 0.02, 20, 800],
]
if is_show: fig = plt.figure();
for k, m, A0, c, et, Nt in params:
dt = et / float(Nt)
df_each = fit_equ.prepare_data(k, m, A0, c, et, Nt)
if is_show: plt.plot(df_each['t'], df_each['x'])
x, xt, xtt = fit_equ.cal_derivatives(df_each, dt, Nt)
X_library, y_library, names = fit_equ.build_library(x, xt, xtt)
coef = fit_equ.fit(X_library, y_library)
coef_res = [(each[0], round(each[1], 4)) for each in list(zip(names, coef.tolist())) if abs(each[1]) >= 1e-3]
coef_res = sorted(coef_res, key=lambda x: abs(x[1]), reverse=True)
m_coef, k_coef = coef_res[0][1], coef_res[1][1]
data.append([m, k, A0, c, k_coef, m_coef, abs(k_coef+k/c)/abs(k/c), abs(m_coef+m/c)/abs(m/c)])
if is_show:
plt.xlabel('Time: t/s', fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel('Displacement: x/m', fontsize=20)
plt.tick_params(labelsize=14)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
df = pd.DataFrame(
data, columns=['m', 'k', 'A0', 'c',
'k_coef', 'm_coef', 'k_coef_err_per', 'c_coef_err_per'])
return df
df = prepare_dataset(is_show=True)
print(df)
Fitting r2 1.0
Fitting r2 1.0
Fitting r2 1.0
Fitting r2 1.0
m k A0 c k_coef m_coef k_coef_err_per c_coef_err_per
0 1.0 1.0 0.10 0.100 -10.0086 -10.0170 0.000860 0.001700
1 0.8 0.5 0.05 0.050 -10.0054 -16.0171 0.000540 0.001069
2 0.1 0.1 0.02 0.004 -25.0214 -25.0428 0.000856 0.001712
3 0.2 0.2 0.07 0.020 -10.0086 -10.0170 0.000860 0.001700
Recover -m/c#
Dimension matrix for input parameters: \(\begin{align} D_{in}= \begin{bmatrix} 1, 1, 0, 1 \\ 0, 0, 1, 0 \\ 0, -2, 0, -1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
Dimension matrix for output parameters: \(\begin{align} D_{out}= \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
Solution space is: \(\begin{align} w &= \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \\ -2 \end{bmatrix} * \gamma + \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 0 \\ -1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
The best basis coefficients are \(\gamma=0\).
The best solution \(w^*\) is \(\begin{align} w^* &= \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 0 \\ -1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
class DimensionlessLearning(object):
'''
Indentify the explicit form one coefficient using dimensionless learning
'''
def __init__(self, df, input_list, output_coef, dimension_info, basis_list):
super(DimensionlessLearning, self).__init__()
self.df = df
self.input_list = input_list
self.output_coef = output_coef
self.X, self.y = self.prepare_dataset()
self.dimension_info, self.basis_list = dimension_info, basis_list
self.basis1_in, self.basis2_in = self.prepare_dimension()
def prepare_dataset(self):
'''
prepare the input and output data
'''
X = self.df[self.input_list].to_numpy()
y = self.df[self.output_coef].to_numpy().reshape(-1, 1)
return X, y
def prepare_dimension(self):
'''
parse dimension for input and output
'''
basis1_in, basis2_in = self.basis_list[0], self.basis_list[1]
return basis1_in, basis2_in
def fetch_coef_pi(self, coef):
'''
parse the combined weights for the input
'''
coef_pi = coef[0] * self.basis1_in + self.basis2_in
return coef_pi
def check_dimension(self, coef):
'''
check whether the basis vectors can formulated as the D_out
'''
coef_pi = self.fetch_coef_pi(coef)
print('[check] coef_pi: \n', coef_pi)
target_D_out = np.dot(self.dimension_info[0], coef_pi)
print('[check] target_D_out: \n', target_D_out)
assert np.array_equal(target_D_out, self.dimension_info[1]), 'Wrong target_D_out!'
def fit_pattern_search(self, seed):
'''
pattern search
'''
def get_coordinates(a, delta):
'''
Build a list to store all possible coordiantes
'''
coord_all = []
for a_ in [a-delta, a, a+delta]:
if [a_] != [a]:
coord_all.append([a_])
return coord_all
def opt(coef):
'''
fit a linear regression
'''
coef_pi = self.fetch_coef_pi(coef)
pi_in = np.prod(np.power(self.X, coef_pi.reshape(-1,)), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
reg =LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False)
reg.fit(pi_in, self.y)
y_pred = reg.predict(pi_in)
r2 = r2_score(self.y, y_pred)
return r2, coef_pi, reg.coef_
np.random.seed(seed)
res, break_points = [], []
a = np.random.choice(np.linspace(-2, 2, 9), 1)[0] # [-2, 2] delta=0.5
# a= 0
coef = np.array([a]).reshape(-1, 1)
iter_num, max_iter, delta = 0, 10, 0.5
while iter_num < max_iter:
candidate_coord = get_coordinates(a, delta)
r2_center, reg_coef_center, coef_w_center = opt(coef)
# print('r2_center', round(r2_center, 2), 'reg_coef_center', [round(each, 2) for each in list(reg_coef_center.reshape(-1,))])
# print('coef_w_center', coef_w_center)
if r2_center < 0.2:
break_points.append([a])
break
r2_bounds_val = []
for [a_] in candidate_coord:
coef_temp = np.array([a_]).reshape(-1, 1)
r2_bound, reg_coef_bound, coef_w_bound = opt(coef_temp)
r2_bounds_val.append(r2_bound)
# sort r2 from high to low
highest_index = np.argsort(r2_bounds_val)[::-1][0]
iter_num += 1
# udpate the center coordiantes when the R2 in the neighborhood is higher
if r2_center < r2_bounds_val[highest_index]:
[a] = candidate_coord[highest_index]
coef = np.array([a]).reshape(-1, 1)
coef_pi = self.fetch_coef_pi(coef)
res_info = {'a': a, 'r2_center': round(r2_bounds_val[highest_index], 4)}
# print('update', res_info)
res.append(res_info)
else:
break
coef_pi = self.fetch_coef_pi(coef)
r2, reg_coef_final, coef_w_final = opt(coef)
return r2, reg_coef_final, coef_w_final
def recover_coef1(seed):
input_list = ['m', 'k', 'A0', 'c']
output_coef = 'm_coef'
D_in = np.mat('1, 0, 0; 1, 0, -2; 0, 1, 0; 1, 0, -1').T
D_out = np.mat('0;, 0; 1')
dimension_info = [D_in, D_out]
basis1_in = np.array([1, 1, 0, -2]).reshape(-1, 1)
basis2_in = np.array([1, 0, 0, -1]).reshape(-1, 1)
basis_list = [basis1_in, basis2_in]
dimensionless_learning = DimensionlessLearning(
df, input_list, output_coef, dimension_info, basis_list)
# dimensionless_learning.check_dimension(coef=[0])
# pattern search
r2, coef, coef_w = dimensionless_learning.fit_pattern_search(seed=seed)
if r2 > 0.8:
print('final r2', r2, coef.flatten(), coef_w)
for i in range(5):
recover_coef1(seed=i)
final r2 0.9999994702111235 [ 1. 0. 0. -1.] [[-1.00155745]]
final r2 0.9999994702111235 [ 1. 0. 0. -1.] [[-1.00155745]]
Recover -k/c#
Dimension matrix for input parameters: \(\begin{align} D_{in}= \begin{bmatrix} 1, 1, 0, 1 \\ 0, 0, 1, 0 \\ 0, -2, 0, -1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
Dimension matrix for output parameters: \(\begin{align} D_{out}= \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ -1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
Solution space is: \(\begin{align} w &= \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \\ -2 \end{bmatrix} * \gamma + \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 1 \\ 0 \\ -1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
The best basis coefficients are \(\gamma=0\).
The best solution \(w^*\) is \(\begin{align} w^* &= \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 1 \\ 0 \\ -1 \end{bmatrix} \end{align}\)
def recover_coef2(seed):
input_list = ['m', 'k', 'A0', 'c']
output_coef = 'k_coef'
D_in = np.mat('1, 0, 0; 1, 0, -2; 0, 1, 0; 1, 0, -1').T
D_out = np.mat('0;, 0; -1')
dimension_info = [D_in, D_out]
basis1_in = np.array([1, 1, 0, -2]).reshape(-1, 1)
basis2_in = np.array([0, 1, 0, -1]).reshape(-1, 1)
basis_list = [basis1_in, basis2_in]
dimensionless_learning = DimensionlessLearning(
df, input_list, output_coef, dimension_info, basis_list)
# dimensionless_learning.check_dimension(coef=[0, 1])
# pattern search
r2, coef, coef_w = dimensionless_learning.fit_pattern_search(seed=seed)
if r2 > 0.8:
print('final r2', r2, coef.flatten(), coef_w)
for i in range(5):
recover_coef2(seed=i)
final r2 0.9999999469825553 [ 0. 1. 0. -1.] [[-1.0008227]]
final r2 0.9999999469825553 [ 0. 1. 0. -1.] [[-1.0008227]]


